



Welcome to the definitive guide on punching presses, an indispensable tool in the modern manufacturing landscape. Whether you're a seasoned professional or new to the world of metal fabrication, understanding the intricacies of punching press technology is crucial for anyone aiming to excel in the manufacturing sector. This article will navigate you through the essentials, from understanding the basic components to exploring the latest advancements in punching press technology.
Have you ever wondered how those intricate shapes in metals are formed? Or how exact cut-outs are created in large sheets of material? The answer lies in a remarkable machine known as the punching press. This equipment is a game-changer in the manufacturing world, especially for those in the 2B sector looking for efficiency and precision.
At its core, the punching press is a machine that uses force to punch holes, shapes, or cut-outs in various materials, primarily metal. This can range from simple circles and rectangles to complex custom designs. The versatility and speed of the punching press make it an indispensable tool in the manufacturing industry, offering both speed and precision without compromising on quality.
But what sets the punching press apart from other metal forming techniques? The key lies in its efficiency and ability to produce parts with smooth, clean edges. This is crucial for manufacturers who demand precision and repeatability in their products. Whether you're dealing with thin sheets or thick plates, the punching press can handle it all, making it a versatile solution for various manufacturing needs.
Moreover, the modern punching press comes equipped with advanced features like computer numerical control (CNC), which allows for greater accuracy and automation. This means that once the design is programmed into the machine, it can produce consistent results at an incredibly high speed, significantly reducing the time and cost associated with traditional methods.
In conclusion, understanding the functionality and advantages of the punching press is essential for anyone involved in the manufacturing sector. Its ability to efficiently create precise shapes and cut-outs in materials has revolutionized the way we approach metal forming and fabrication. Stay tuned as we delve deeper into the specifics and parameters that make this machine a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.
Diving deeper into the anatomy of a punching press, let’s explore the core components that make this machine not just functional but exceptionally efficient. These components include the frame, clamps, and dies, each playing a pivotal role in the operation of a punching press.
Firstly, the frame acts as the backbone of the punching press. It supports all other components and withstands the operational stresses. Typically made from high-strength steel, the frame ensures the stability and durability of the machine. It's designed to absorb the force exerted during the punching process, preventing any deformation and maintaining the precision of the punch.
Next, we have the clamps. These are crucial for securing the material in place during the punching process. Without proper clamping, materials could move during punching, leading to inaccuracies and waste. Clamps must be both strong and adjustable to accommodate different thicknesses and types of materials, ensuring that they are held firmly in place, thus enhancing the precision and efficiency of the punching process.
Last but not least are the dies. Dies are custom-made tools that do the actual punching. They come in various shapes and sizes, depending on the desired outcome of the punch. The die and the punch work in tandem: while the punch exerts the downward force, the die provides the necessary resistance to shape the material. The precision of the dies directly influences the quality and accuracy of the final product, making them one of the most critical components of the punching press.
Understanding these core components is essential for anyone looking to leverage the full potential of their punching press. The interplay between the frame, clamps, and dies not only determines the capability of the press but also impacts the quality, speed, and efficiency of the production process. As we move forward, we will delve into the operational parameters that govern the punching press, providing a clearer understanding of how these components come together to perform the task at hand.
In the realm of punching presses, the frame is not just a static support structure; it's a vital component that influences the machine's functionality, accessibility, and stability. Predominantly, there are two types of frames that are central to the design of punching presses: C-Frame and H-Frame. Each type has its unique advantages and applications, making them suitable for different manufacturing environments.
Firstly, let's talk about the C-Frame presses. As the name suggests, these machines have a frame that resembles the letter 'C'. This design offers excellent accessibility, as three sides of the press are open, allowing for easy material handling and tool changes. The C-Frame press is highly favored for its space-saving design, making it an ideal choice for smaller workshops or facilities with limited floor space. However, it's worth noting that while C-Frames are versatile and accessible, they might not be the best fit for extremely heavy or large-scale operations due to their open structure, which can limit their ability to handle high forces without deflection.
On the other hand, H-Frame presses feature a more robust and enclosed structure, resembling the letter 'H'. This design offers superior strength and rigidity, making H-Frame presses suitable for heavy-duty operations that require high pressure. The increased stability reduces the chances of deflection and allows for more precise and consistent punching. Although H-Frame presses take up more space and offer less accessibility than their C-Frame counterparts, they are indispensable for tasks that demand high precision and force.
Choosing between a C-Frame and an H-Frame press depends on several factors, including the nature of the manufacturing tasks, the space available, and the desired precision and capacity. While C-Frames are excellent for quick, light-to-medium jobs and offer greater accessibility, H-Frames stand out in high-volume, high-pressure environments where precision and durability are paramount.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between C-Frame and H-Frame punching presses is crucial for manufacturers looking to make informed decisions about which machine best fits their needs. Each frame type brings distinct advantages to the table, influencing the overall performance and suitability of the punching press for specific applications.
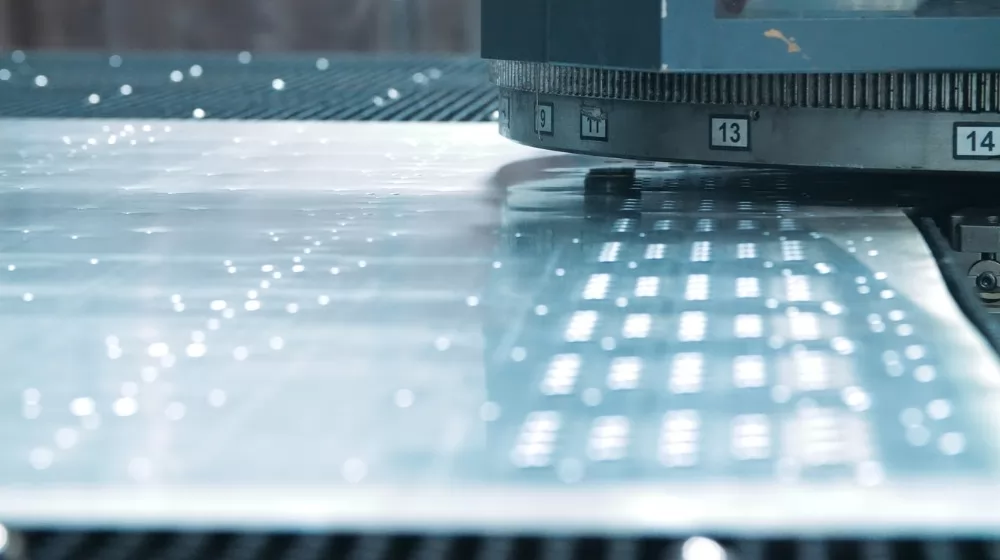
In the anatomy of a punching press, if the frame is the skeleton and the clamps are the muscles, then surely, the dies are the heart. These crucial components are where the magic happens, transforming plain sheets into precise parts with clean cuts and shapes. Understanding the types of dies and their functions is essential for anyone looking to maximize the capabilities of their punching press.
There are several types of dies, each designed for specific tasks and materials. The most common include blanking dies, forming dies, and progressive dies:
Each type of die plays a specific role in the manufacturing process, contributing to the versatility and efficiency of the punching press. The choice of die depends on the material, the complexity of the part, and the production volume. For instance, while blanking dies are great for simple, flat parts, forming dies are chosen for more complex geometries, and progressive dies are ideal for high-volume production.
In conclusion, the dies are indeed the heart of the punching press, pumping life into raw materials by transforming them into functional parts. By selecting the appropriate type of die for each task, manufacturers can ensure high-quality results, efficient production, and minimal material waste, thereby optimizing the performance and output of their punching presses.
The function and efficiency of a punching press are significantly influenced by its drive mechanism. This component is what powers the machine, enabling it to exert the necessary force to punch through materials. Understanding the different drive mechanisms available and how they affect the performance of a punching press is crucial for selecting the right equipment for your manufacturing needs.
There are primarily three types of drive mechanisms used in punching presses: mechanical, hydraulic, and servo-electric. Each type comes with its own set of advantages and is suited to different types of tasks:
The choice of drive mechanism will affect not just the performance of the punching press but also its operational costs and maintenance needs. Mechanical drives, while fast and reliable, may not offer the same level of control as hydraulic drives. Hydraulic presses, on the other hand, are more versatile but also require more maintenance. Servo-electric drives offer the best of both worlds but at a higher initial cost.
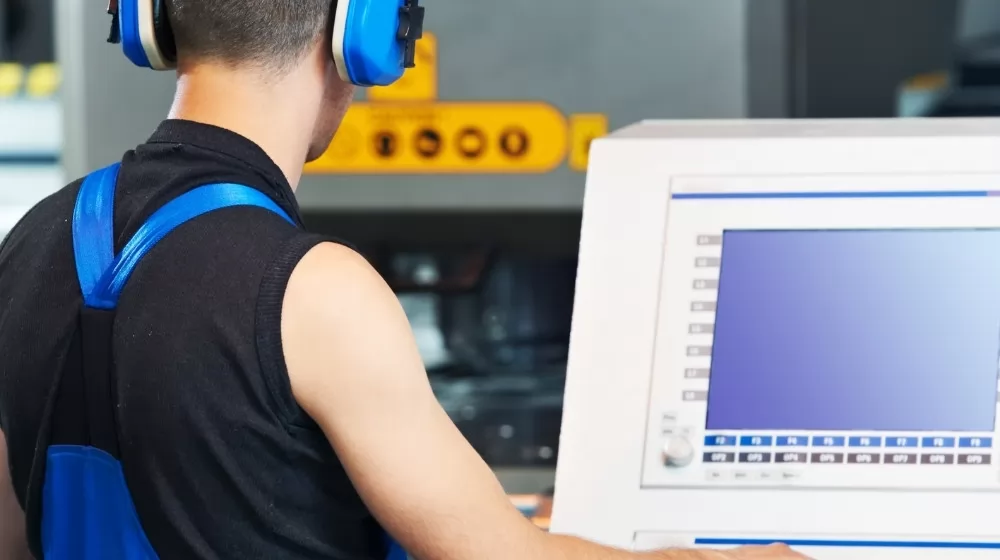

When it comes to selecting a punching press, one of the primary decisions manufacturers face is choosing between mechanical and hydraulic presses. Both types have their unique advantages and are suited to different manufacturing environments and needs. A comparative analysis of mechanical versus hydraulic presses can help clarify which option might be the best fit for your specific requirements.
Speed and Efficiency: Mechanical presses are generally faster than hydraulic presses because they operate on a fixed cycle, powered by the momentum of the flywheel. This makes them ideal for high-volume, repetitive tasks where speed is of the essence. On the other hand, hydraulic presses are slower but offer greater flexibility in terms of speed adjustment, which can be beneficial for tasks requiring precision and varying force.
Power and Control: Hydraulic presses provide more control over the ram's movement and pressure, allowing for more precise operations. This is particularly useful for complex shapes or materials requiring specific pressures. Mechanical presses, while less flexible in terms of pressure control, provide consistent, high-speed power for straightforward punching tasks.
Maintenance and Cost: In terms of maintenance, hydraulic presses tend to require more due to their fluid-based system, which can be prone to leaks and contamination. Mechanical presses typically have fewer maintenance needs but can be more challenging to repair if a breakdown occurs. Initially, mechanical presses might be less expensive than hydraulic ones, but the overall cost will also depend on operational needs and maintenance expenses.
Versatility and Application: Hydraulic presses are more versatile, able to handle a wider range of materials and thicknesses. They are particularly suited for applications requiring deep drawing, molding, or more nuanced pressure adjustments. Mechanical presses, however, excel in applications that require high-speed stamping and cutting of uniform parts.
In conclusion, the choice between mechanical and hydraulic presses depends on the specific needs of your manufacturing process. If you prioritize speed and efficiency for high-volume production, a mechanical press might be the best choice. However, if your operations require versatility, precise control, and are less concerned with speed, a hydraulic press could be the more suitable option. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each type can lead to a more informed and effective decision for your punching press requirements.
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology has revolutionized many aspects of manufacturing, and punching presses are no exception. The integration of CNC into punching presses has brought unprecedented levels of accuracy, efficiency, and flexibility to the metal fabrication process. Understanding the role of CNC in modern punching presses is essential for manufacturers looking to stay competitive in today’s market.
CNC technology allows for the precise control of the punching press, enabling operators to program the desired shapes, sizes, and patterns into the machine. This level of precision is especially beneficial when producing complex parts or working with delicate materials. CNC punching presses can automatically adjust the position and speed of the punch, ensuring high levels of accuracy and consistency, which are difficult to achieve with manual controls.
Moreover, the automation provided by CNC technology significantly reduces the time and labor required to set up and operate the punching press. This can lead to substantial cost savings and increased production capacity. The ability to quickly and easily modify programs also makes CNC punching presses highly adaptable to changing production demands, enhancing their efficiency and reducing downtime.
Another significant advantage of CNC in punching presses is the optimization of material usage. CNC systems can calculate the most efficient layout for punching, minimizing waste and maximizing the use of materials. This not only reduces costs but also supports sustainable manufacturing practices.
In conclusion, the role of CNC in modern punching presses is indispensable. It provides manufacturers with the tools to produce high-quality parts efficiently and cost-effectively. By leveraging the precision, flexibility, and automation offered by CNC technology, businesses can enhance their production processes, reduce waste, and meet the evolving needs of their customers. As we continue to witness advancements in CNC and punching press technologies, the potential for innovation and improvement in manufacturing is boundless.
The performance of a punching press is heavily influenced by the type and characteristics of the material being processed. Factors such as thickness, hardness, and other material attributes play crucial roles in determining the optimal punching parameters. For instance, harder metals require more force to punch but can endure higher speeds without deforming, whereas softer metals may punch easily but require slower speeds to maintain accuracy.
Understanding the balance between force, speed, and accuracy is essential for efficient punching press operations. The required force depends on the material's thickness and hardness; the speed must be adjusted to ensure clean cuts without damaging the material; and accuracy is crucial for the final product's quality.
The punching force can be calculated based on the material’s thickness and ultimate tensile strength. This calculation helps in selecting the right punching press and setting the proper parameters to ensure efficient and effective punching operations.
The trade-off between speed and precision is a critical consideration. High-speed operations can lead to decreased accuracy, so it’s important to find a balance that maintains quality while optimizing production time.
The design of the die and punch directly impacts the quality of the punched part. Factors such as die clearance and punch edge sharpness are crucial for achieving clean cuts and extending tool life.
Die clearance is a critical parameter that should be adjusted according to the material thickness. Proper clearance minimizes burrs and extends the life of the die and punch.
Choosing between standard and custom dies depends on the specific requirements of the punching operation. While standard dies are cost-effective and readily available, custom dies offer greater flexibility for unique or complex shapes.

Punching presses have a wide range of applications across various industries. In the automotive sector, they are used to create precise parts like brackets, panels, and various body components. In aerospace, they help manufacture critical, high-precision components. This versatility demonstrates the essential role of punching presses in modern manufacturing.
Exploring case studies reveals the innovative uses of punching presses in industry. For instance, in the production of energy-efficient building materials or in creating intricate designs for electronic components, punching presses have enabled companies to increase efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance product quality.
The future of punching press technology is marked by trends such as increased automation, integration of AI for predictive maintenance, and the use of more durable, lightweight materials. These innovations are making punching presses more efficient, accurate, and adaptable to the changing needs of industries.
Automation and robotics are transforming punching press operations, enabling higher precision, faster production speeds, and reduced labor costs. Robotic arms equipped with sensors can feed material, operate the press, and remove finished products, streamlining the entire manufacturing process.
In response to growing environmental concerns, the punching press industry is moving towards green manufacturing practices. This includes developing energy-efficient machines, reducing waste through improved material utilization, and recycling scrap materials. By focusing on sustainability, manufacturers are not only reducing their environmental impact but also cutting costs and improving efficiency.
Selecting the appropriate punching press for your manufacturing operations is a decision that can significantly impact your productivity, quality, and bottom line. To ensure you make the best choice, consider several key factors tailored to your specific needs.
The type of materials you plan to punch plays a crucial role in selecting the right press. Consider the thickness, hardness, and overall size of the materials. Different presses are better suited for different materials and thicknesses, so understanding your material needs will help narrow down your options.
Your production volume is another critical factor. If you require high-speed, high-volume production, a mechanical press may be more suitable. For lower volumes or more varied production, a hydraulic press might be the better choice due to its versatility and control.
The complexity of the parts you need to produce will also influence your choice. If you need to produce complex parts with high precision, a CNC punching press might be necessary. These presses offer greater control and flexibility, allowing for intricate designs and consistent quality.
The available space in your facility and power constraints are practical considerations that can't be overlooked. Ensure the press you choose fits in your allocated space and that your facility can provide the required power supply.
Finally, budget is a crucial factor. Consider not only the initial cost but also the long-term operational costs, including maintenance, tooling, and energy consumption. Opt for a punching press that offers the best balance between initial investment and ongoing expenses.
In conclusion, the journey through the world of punching presses reveals a landscape filled with innovation, efficiency, and precision. As we've explored the various components, types, and applications, it's clear that the right punching press can significantly elevate your manufacturing capabilities. For those seeking the pinnacle of punching press technology, look no further than JDM, the industry's leading manufacturer. Our state-of-the-art machines are designed with your manufacturing success in mind, ensuring reliability, precision, and efficiency. Discover how JDM can transform your production processes and contribute to your success. Visit our global website at https://www.jdmpresses.com/ to explore our world-class solutions and start your journey towards manufacturing excellence.